Welcome, urban transformation architects and resilience innovators! We stand at the threshold of a profound reimagining of our cities—not as static constructions of concrete and steel, but as dynamic, adaptive ecosystems capable of withstanding, responding to, and evolving through the unprecedented challenges of our era.
Reimagining Urban Resilience for Tomorrow’s World
Resilience in smart cities transcends conventional engineering—it represents a city’s dynamic capacity to resist, absorb, and evolve in response to external forces while preserving its vital functions. This concept has undergone a remarkable metamorphosis, moving beyond traditional approaches to embrace sophisticated AI-driven technologies that amplify a city’s adaptive capabilities.
Smart resilient cities function as intelligent organisms, where information and communication technologies form the neural network connecting traditional infrastructures, creating responsive urban ecosystems. This symbiosis yields not merely smarter cities, but profoundly more resilient ones—capable of anticipating, withstanding, and recovering from the multifaceted challenges of our rapidly changing world.
The imperative for resilience extends beyond technical considerations to the very cornerstone of sustainable urban development and quality of life. A resilient city stands as a guardian of continuity, minimising disruption while ensuring essential services remain accessible during times of stress. Research illuminates five critical pillars supporting this urban resilience architecture:
- Inclusive Engagement: Creating participatory frameworks that incorporate diverse voices in resilience planning
- Collaborative Governance: Fostering partnerships across public, private, and community stakeholders
- Sustainable Systems: Developing infrastructure that balances immediate needs with long-term environmental stewardship
- Adaptive Management: Implementing flexible governance structures that can evolve with emerging challenges
- Human-Centric Focus: Prioritizing public satisfaction and quality of life in resilience strategies
These elements must be woven together through strategic planning and synchronised urban systems, creating a tapestry of resilience that spans technological, social, and ecological dimensions.
Climate Volatility: The Ultimate Stress Test for Urban Electrical Networks
Our changing climate poses perhaps the most profound challenge to urban infrastructure, introducing transformative pressures across global energy systems. The manifestations of this challenge arrive as extreme weather events that test the very foundations of our cities:
- Devastating Storms: High-intensity weather events that compromise structural integrity, such as Hurricane Ida in 2021 which caused widespread power outages in New Orleans
- Catastrophic Flooding: Rising waters that threaten low-lying infrastructure, exemplified by the 2021 floods in Zhengzhou, China, which inundated subway systems
- Crippling Ice Formations: Heavy accumulations that burden transmission lines beyond design parameters, as seen in the 2021 Texas power crisis
- Extended Droughts: Water scarcity affecting cooling systems and agriculture, like the ongoing megadrought in the Western United States
- Destructive Tornadoes: Extreme winds that can devastate grid sections in minutes, as demonstrated by the December 2021 tornado outbreak in the Midwest and Southern United States

Rising global temperatures further amplify these stresses, triggering heatwaves that place immense strain on power grids as cooling demand surges beyond designed capacities.
These challenges strike at the heart of our electrical systems—the lifeblood of modern urban environments. Extreme weather events directly assault physical infrastructure, damaging transmission lines, utility poles, and substations, often resulting in extended power outages that paralyse city functions.
The interconnected nature of urban infrastructure creates cascade effects, where electrical failures disrupt transportation networks, water treatment facilities, healthcare systems, and digital communications. This transformation of localised disruptions into systemic urban crises underscores one critical truth: resilient electrical systems are fundamental to the continued functioning of smart cities in an era of climate uncertainty.
The Intelligence Revolution: AI as the Architect of Resilience
Artificial intelligence emerges as the master architect in designing resilient cities, offering unprecedented capabilities to anticipate, adapt to, and overcome urban challenges. Three transformative applications stand at the forefront of this revolution:
Predictive Intelligence: Foreseeing Infrastructure Needs
AI algorithms serve as urban soothsayers, analysing vast data streams—from grid sensors to maintenance logs—to predict potential failures before they occur. For example, New York City’s Department of Environmental Protection uses machine learning models to predict water main breaks, allowing for proactive maintenance that prevents disruptions before they impact residents.
By enabling preventative intervention, these systems dramatically reduce costly outages, minimise service disruptions, and enhance quality of life for urban dwellers. The city becomes not just smart, but anticipatory—capable of addressing weaknesses before they compromise essential functions.
Adaptive Energy Orchestration: The Self-Balancing Grid
AI acts as the conductor of a self-balancing energy network, aligning supply and demand with precision. The Grid Singularity project in Europe demonstrates this by using AI to create a decentralized energy exchange platform, enabling more efficient integration of renewable energy sources while maintaining grid stability under varying conditions.
Through continuous analysis of real-time data from smart meters, AI identifies inefficiencies, predicts demand fluctuations, and optimises distribution accordingly. Perhaps most critically, AI orchestrates the management of microgrids—localised energy networks capable of autonomous operation during disruptions—ensuring that hospitals, emergency services, and critical infrastructure maintain power continuity even when the main grid falters.
Real-Time Responsiveness: The Urban Nervous System
In crisis situations—from severe weather to major infrastructure failures—AI synthesises data from distributed sensors, social media, and emergency services, enabling swift, coordinated responses. Tokyo’s disaster prevention system, which uses AI to analyze social media posts during earthquakes, exemplifies this approach to creating urban environments that respond intelligently to evolving threats.
This comprehensive awareness enables:
- Enhanced Emergency Coordination: Deploying resources precisely where and when they’re needed most
- Predictive Impact Modeling: Anticipating cascade effects before they manifest
- Optimal Resource Allocation: Directing emergency personnel and equipment with unprecedented efficiency
- Vulnerable Population Protection: Identifying and prioritizing assistance to at-risk communities
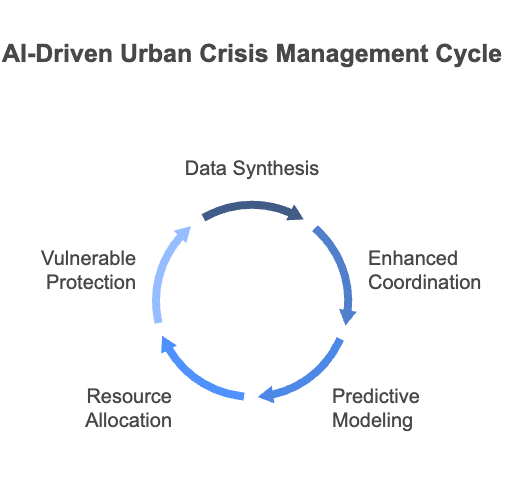
Even during crisis management, these systems continue to support infrastructure resilience through predictive maintenance, ensuring that secondary failures don’t compound an already challenging situation
The Blueprint for Urban Evolution: Resilience Strategies

Creating a truly resilient smart city demands a symphony of approaches that unify technical innovation with thoughtful urban planning. Key strategies forming this blueprint include:
Infrastructure Fortification
Rotterdam’s climate adaptation strategy exemplifies this approach, including raising the ground level in flood-prone areas and creating water plazas that double as retention basins during heavy rainfall. This physical hardening represents the first line of defense against climate volatility and other external stresses.
Renewable Energy Ecosystem
Copenhagen’s goal to become carbon-neutral by 2025 involves developing a diverse energy portfolio including wind, solar, and biomass, optimized by AI systems. This diversification creates redundancy and flexibility, key components of resilient systems that can withstand supply disruptions.
Intelligent Grid Orchestration
Singapore’s Energy Market Authority is implementing an AI-driven energy distribution system to enhance grid reliability and efficiency. These systems transform static infrastructure into dynamic, responsive networks that adapt in real-time to changing demands and conditions.
Anticipatory Maintenance
Barcelona’s smart city initiative includes sensors throughout the water distribution network to detect leaks and predict maintenance needs. This shift from reactive to proactive maintenance fundamentally transforms the economics and reliability of urban infrastructure.
Resilience Islands (Microgrids)
San Diego’s implementation of microgrids, including at the University of California San Diego campus, demonstrates how localized energy ecosystems can maintain critical functions during broader system disruptions, creating islands of stability in seas of uncertainty.
Nature-Technology Partnership
China’s “sponge cities” initiative integrates green infrastructure with advanced water management technologies to enhance flood resilience. This integration recognizes that resilience emerges from the synergy between engineered and natural systems.

Data-Driven Urban Intelligence
Helsinki’s 3D city model combines various data sources to inform urban planning decisions and improve energy efficiency. This intelligence layer transforms passive infrastructure into learning systems that evolve with each challenge they face.
The successful implementation of these strategies requires a profound understanding of how climate change pressures, electrical infrastructure, and AI converge. This holistic perspective enables cities to develop integrated approaches that address vulnerabilities across multiple dimensions simultaneously.
The Path Forward: From Vision to Reality
Artificial intelligence stands as the cornerstone of urban resilience, transforming how we predict failures, balance energy demand, and orchestrate real-time emergency responses. By harnessing AI’s analytical prowess and predictive capabilities, cities evolve from passive environments to proactive ecosystems, shaping their futures amidst uncertainty.
In the next chapter, we’ll delve into real-world implementations in pioneering cities like Rotterdam and New York, examining how they use AI-driven strategies to create truly resilient systems—not as hypothetical ideas, but as living laboratories defining the future of urban resilience.
The journey toward urban resilience is not merely a technical challenge but a profound opportunity to reimagine our relationship with the built environment. As we construct the cities of tomorrow, we’re not merely building infrastructure—we’re crafting living systems capable of learning, adapting, and thriving through each new challenge. This is the promise of smart city resilience: urban environments that don’t just survive disruptions but emerge stronger, more sustainable, and more human-centric with every test they face.
